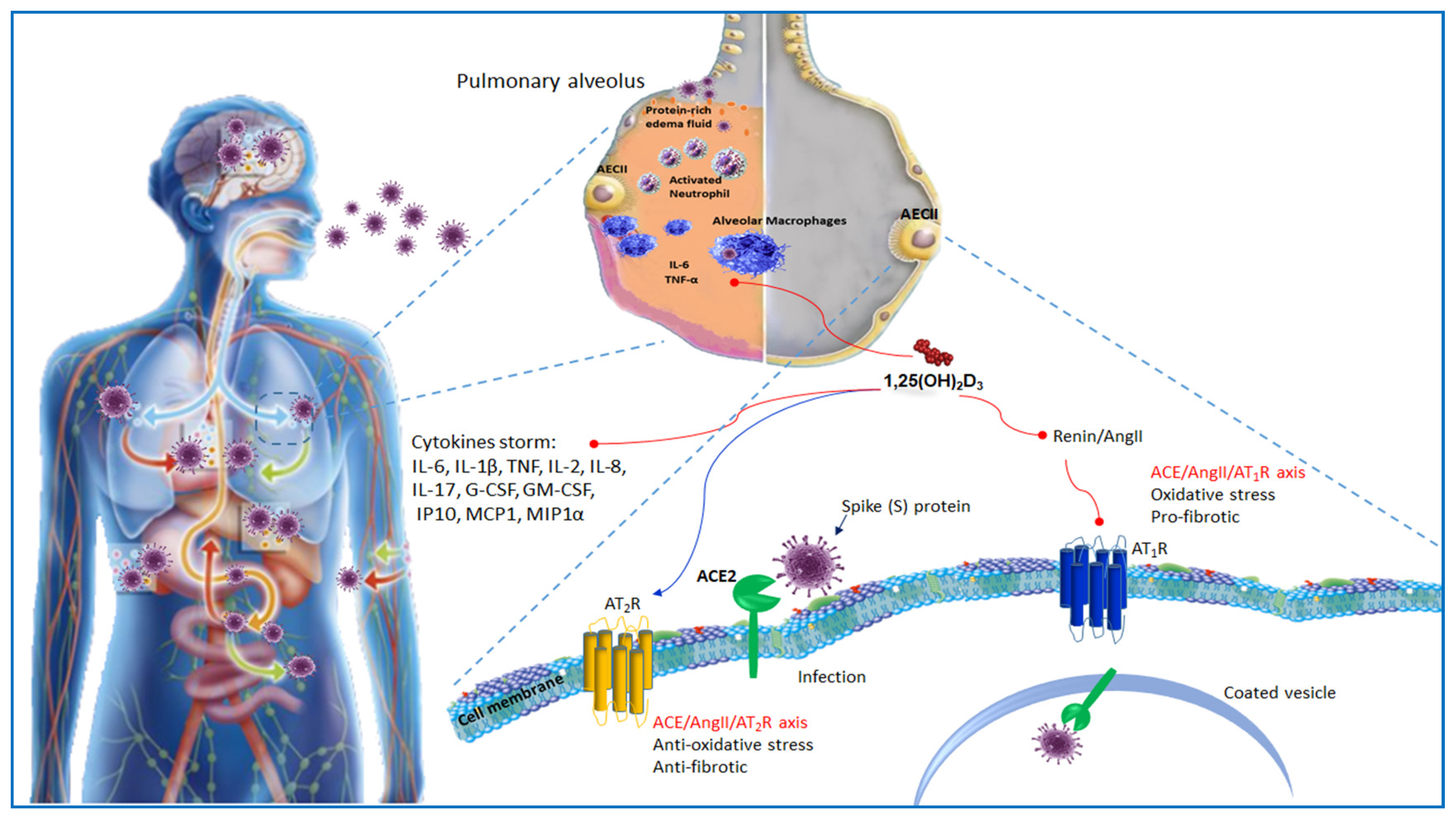
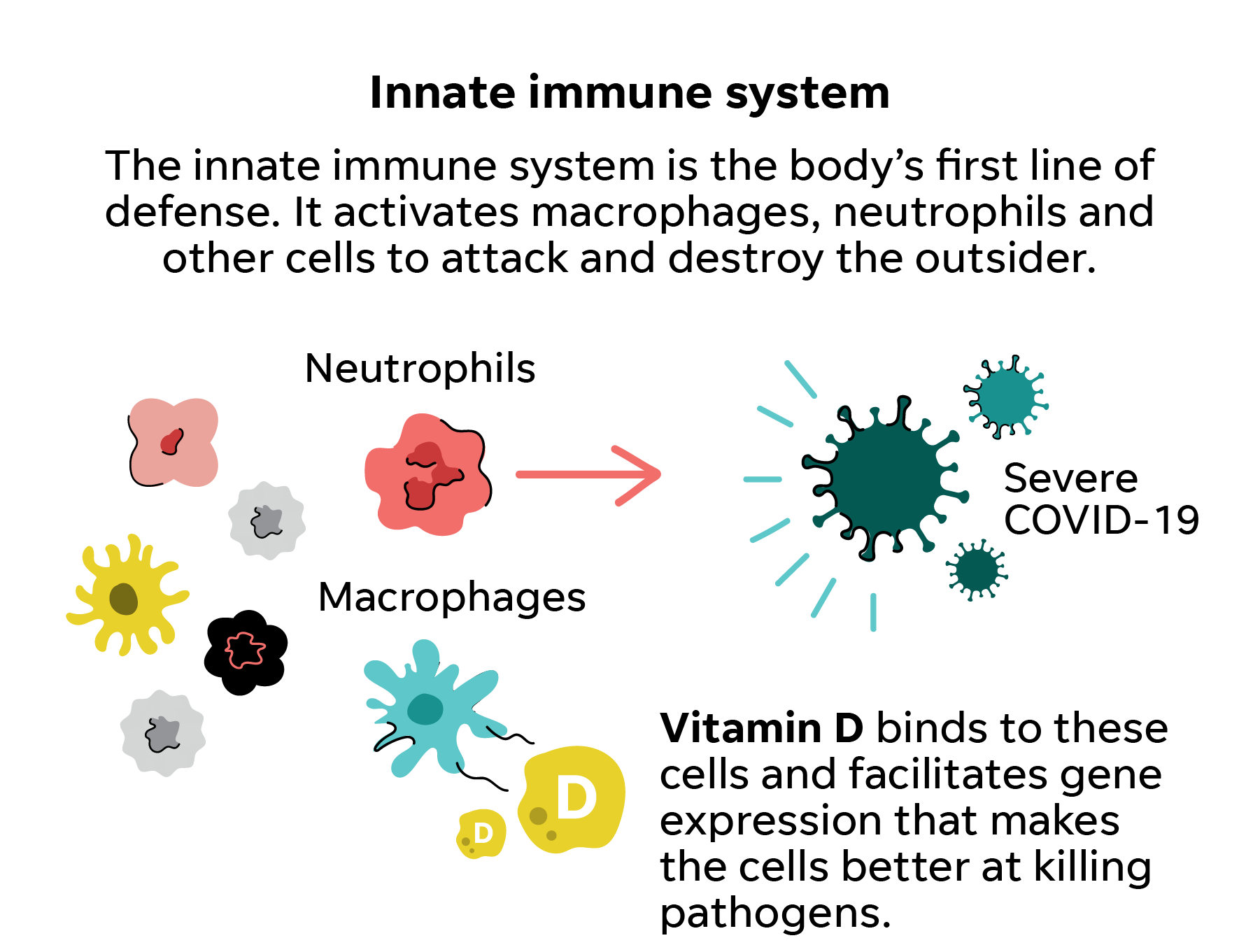
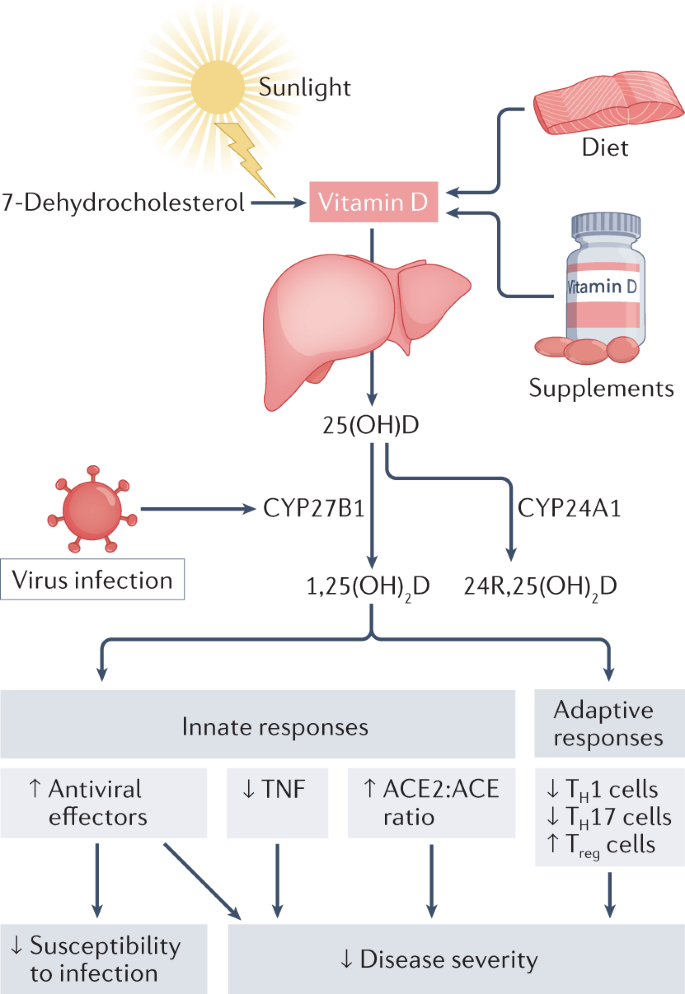
Vitamin D and COVID-19: evidence and recommendations for supplementation | Royal Society Open Science

Influence of Vitamin D3 Levels and T Cell-Related Cytokines in Human Milk on Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection in Lactating Women | Breastfeeding Medicine

Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D - ScienceDirect

Immuno | Free Full-Text | Vitamin D Immune-Mediated Responses and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Clinical Implications in COVID-19
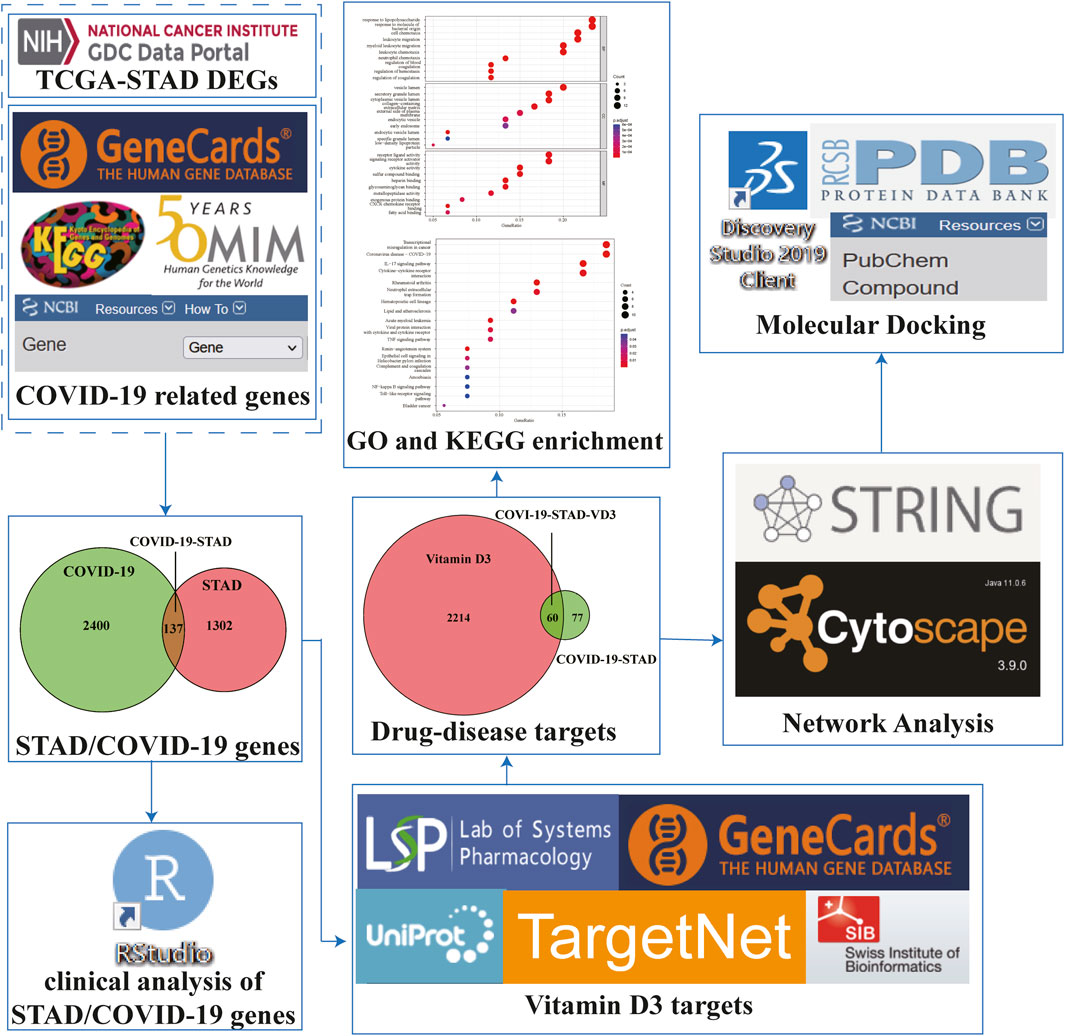
Frontiers | Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Analyses Identify Intersection Genes of Vitamin D3 and COVID-19 as Potential Therapeutic Targets

Vitamin D and COVID-19: evidence and recommendations for supplementation | Royal Society Open Science
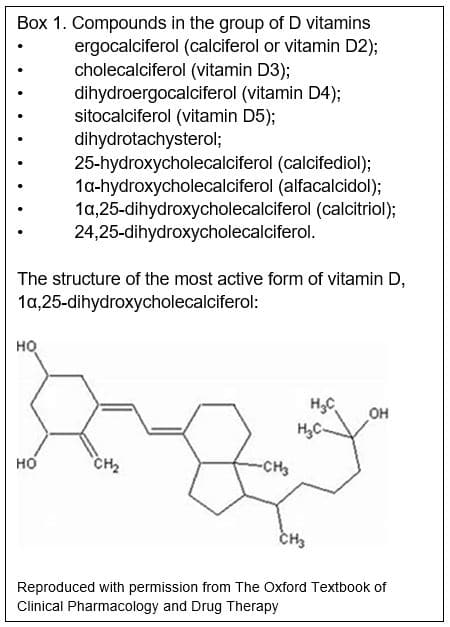
Vitamin D: A rapid review of the evidence for treatment or prevention in COVID-19 - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine

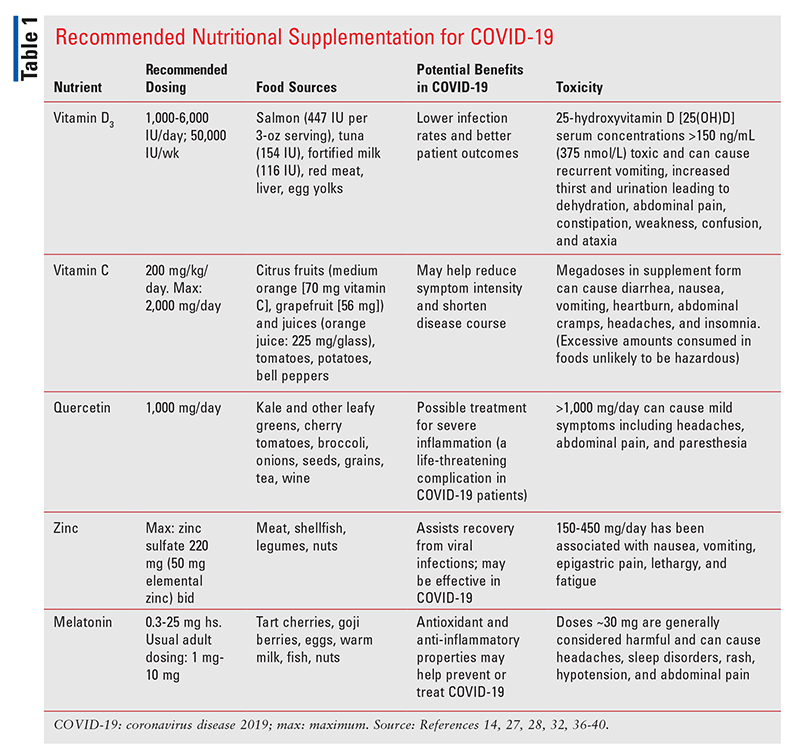
The potential benefits of Vitamin D3, Zinc, Vitamin C and Melatonin supplementation during the COVID-19 pandemic. - Benessere Clinic

Vitamin D3 for reducing mortality from cancer and other outcomes before, during and beyond the COVID‐19 pandemic: A plea for harvesting low‐hanging fruit - Brenner - 2022 - Cancer Communications - Wiley Online Library
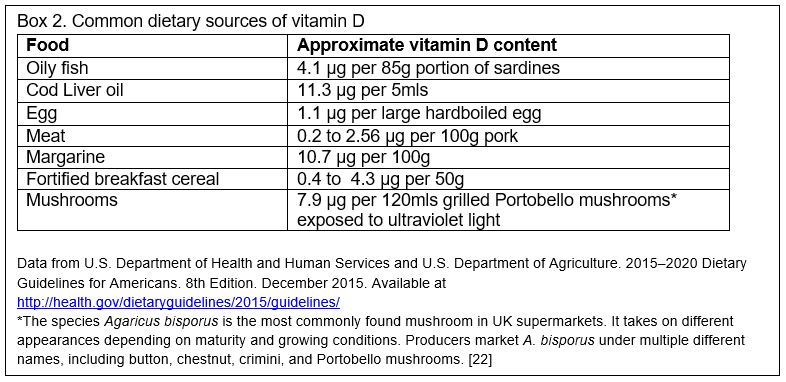
Vitamin D: A rapid review of the evidence for treatment or prevention in COVID-19 - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
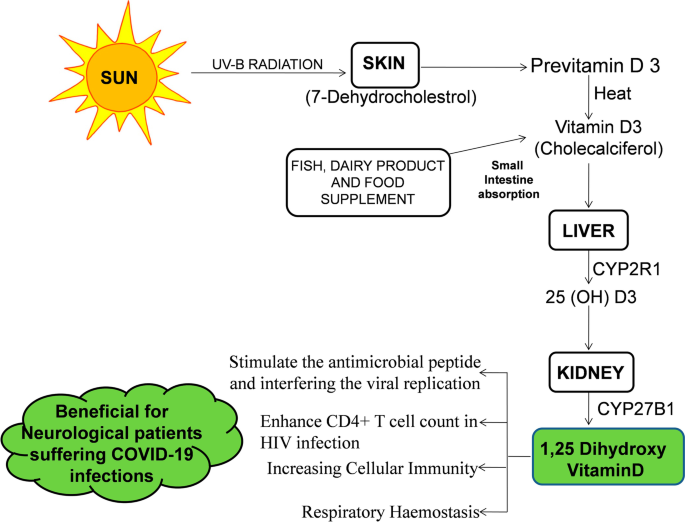
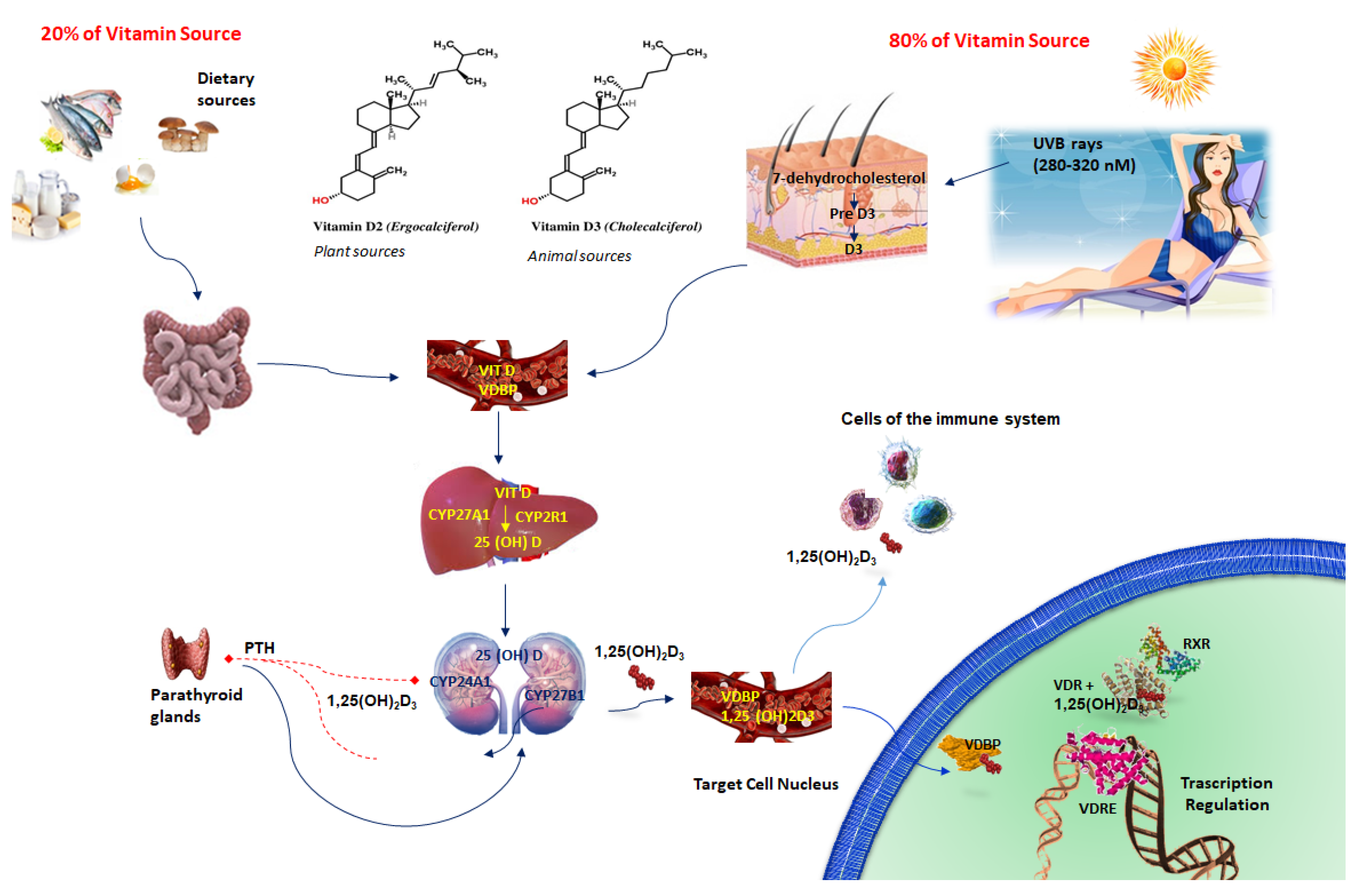
A review article on neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory role of vitamin-D3 in elderly COVID-19 patients | The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery | Full Text
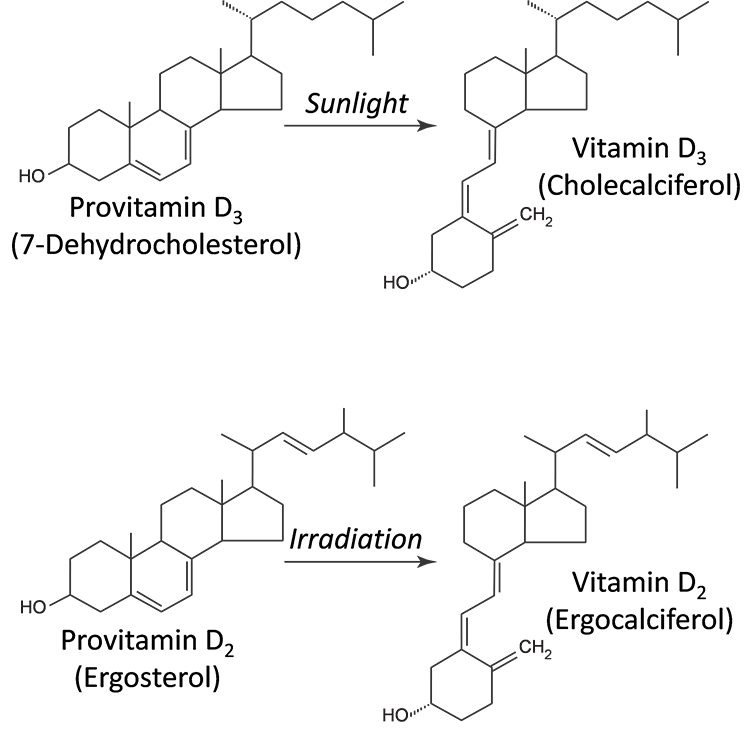
Brain Sciences | Free Full-Text | Potential Role of Vitamin D in the Elderly to Resist COVID-19 and to Slow Progression of Parkinson's Disease
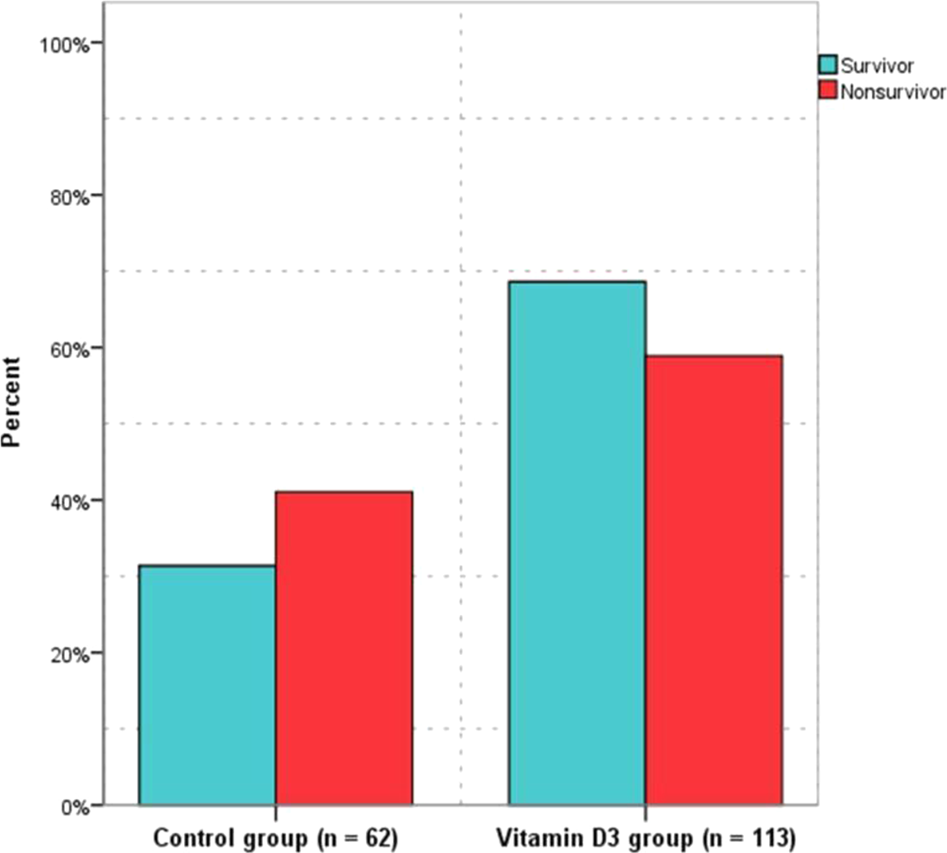
The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D3 on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: an observational cohort study | European Journal of Clinical Nutrition